Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Optics Valley Laboratory, Wuhan 430074, China
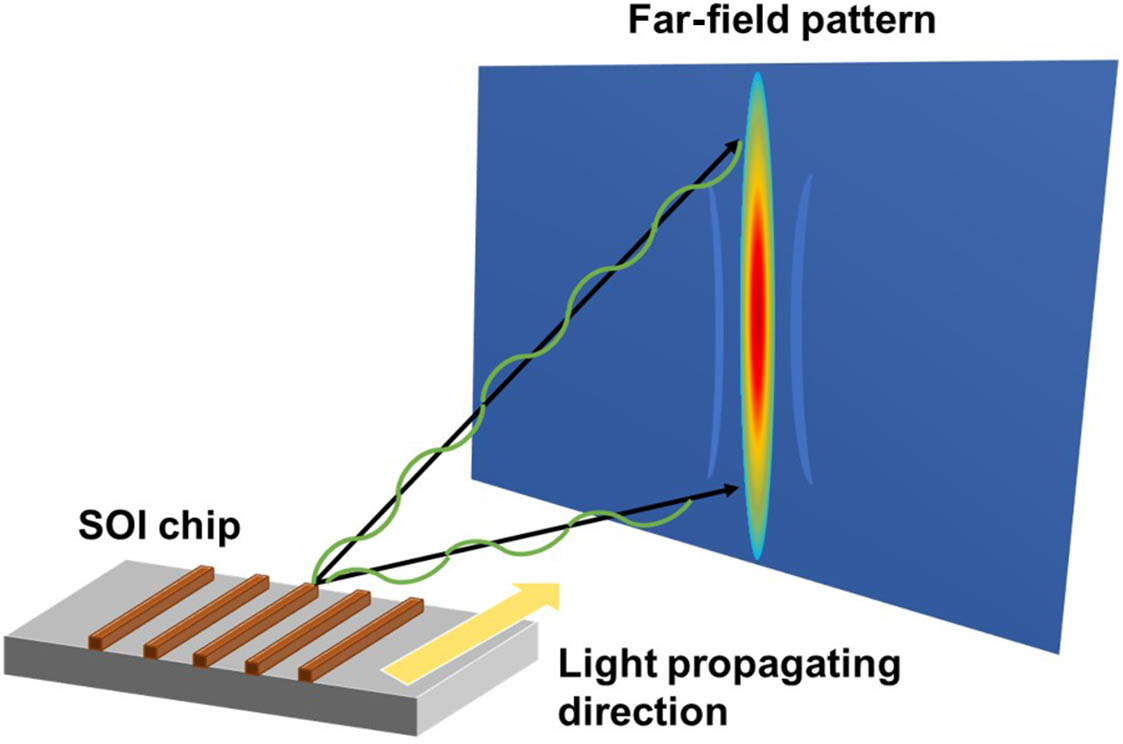
In recent years, optical phased arrays (OPAs) have attracted great interest for their potential applications in light detection and ranging (LiDAR), free-space optical communications (FSOs), holography, and so on. Photonic integrated circuits (PICs) provide solutions for further reducing the size, weight, power, and cost of OPAs. In this paper, we review the recent development of photonic integrated OPAs. We summarize the typical architecture of the integrated OPAs and their performance. We analyze the key components of OPAs and evaluate the figure of merit for OPAs. Various applications in LiDAR, FSO, imaging, biomedical sensing, and specialized beam generation are introduced.
optical phased arrays LiDAR silicon photonics beam steering photonic integration Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(2): 020041
光学 精密工程
2023, 31(15): 2295
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 Department of Chemistry, School of Science, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan
3 CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-Intense Laser Science, Shanghai 201800, China
Among currently available optical spectroscopic methods, Raman spectroscopy has versatile application to investigation of dynamical processes of molecules leading to chemical changes in the gas and liquid phases. However, it is still a challenge to realize an ideal standoff coherent Raman spectrometer with which both high temporal resolution and high-frequency resolution can be achieved, so that one can remotely probe chemical species in real time with high temporal resolution while monitoring the populations in their respective rovibronic levels in the frequency domain with sufficiently high spectral resolution. In the present study, we construct an air-laser-based Raman spectrometer, in which near-infrared femtosecond (fs) laser pulses at 800 nm and cavity-free picosecond N2+ air-laser pulses at 391 nm generated by the filamentation induced by the fs laser pulses are simultaneously used, enabling us to generate a hybrid ps/fs laser source at a desired standoff position for standoff surveillance of chemical and biochemical species. With this prototype Raman spectrometer, we demonstrate that the temporal evolution of the electronic, vibrational, and rotational states of N2+ and the coupling processes of the rovibrational wave packet of N2 molecules can be probed.
Ultrafast Science
2022, 2(1): 9867028
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Materials Laser Processing and Modification, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 RIKEN Center for Advanced Photonics, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan
3 School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
4 State Key Lab of Metal Matrix Composites, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
![]()
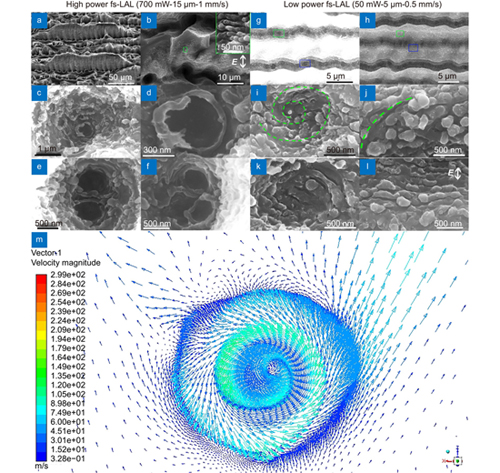
![]() Orientations of laser induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) are usually considered to be governed by the laser polarization state. In this work, we unveil that fluid dynamics induced by femtosecond (fs) laser ablation in liquid (fs-LAL) can easily break this polarization restriction to produce irregular circular-LIPSS (CLIPPS) and crisscross-LIPSS (CCLIPSS). Fs laser ablation of silicon in water shows formation of diverse LIPSS depending on ablation conditions. At a high power of 700 mW (repetition rate of 100 kHz, pulse duration of 457 fs and wavelength of 1045 nm), single/twin CLIPSS are produced at the bottom of macropores of several microns in diameter due to the formation of strong liquid vortexes and occurrence of the vortex shedding effect. Theoretical simulations validate our speculation about the formation of liquid vortex with an ultrahigh static pressure, which can induce the microstructure trenches and cracks at the sidewalls for fs-LAL of Si and tungsten (W) in water, respectively. At a low power of 50 mW, weak liquid vortexes are produced, which only give birth to curved LIPSS in the valleys of grooves. Consequently, it is deduced that liquid vortex plays a crucial role in the formation of macropores. Mountain-like microstructures induce complex fluid dynamics which can cause the formation of CCLIPSS on them. It is believed that liquid vortexes and fluid dynamics presented in this work open up new possibilities to diversify the morphologies of LIPSS formed by fs-LAL.
Orientations of laser induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) are usually considered to be governed by the laser polarization state. In this work, we unveil that fluid dynamics induced by femtosecond (fs) laser ablation in liquid (fs-LAL) can easily break this polarization restriction to produce irregular circular-LIPSS (CLIPPS) and crisscross-LIPSS (CCLIPSS). Fs laser ablation of silicon in water shows formation of diverse LIPSS depending on ablation conditions. At a high power of 700 mW (repetition rate of 100 kHz, pulse duration of 457 fs and wavelength of 1045 nm), single/twin CLIPSS are produced at the bottom of macropores of several microns in diameter due to the formation of strong liquid vortexes and occurrence of the vortex shedding effect. Theoretical simulations validate our speculation about the formation of liquid vortex with an ultrahigh static pressure, which can induce the microstructure trenches and cracks at the sidewalls for fs-LAL of Si and tungsten (W) in water, respectively. At a low power of 50 mW, weak liquid vortexes are produced, which only give birth to curved LIPSS in the valleys of grooves. Consequently, it is deduced that liquid vortex plays a crucial role in the formation of macropores. Mountain-like microstructures induce complex fluid dynamics which can cause the formation of CCLIPSS on them. It is believed that liquid vortexes and fluid dynamics presented in this work open up new possibilities to diversify the morphologies of LIPSS formed by fs-LAL.
circular LIPSS crisscross LIPSS laser ablation in liquid femtosecond laser ablation in water liquid vortex vortex shedding Opto-Electronic Advances
2022, 5(2): 210066
山东理工大学 物理与光电工程学院, 山东 淄博 255000
磁场的传感测量在相关领域具有重要应用。利用磁流体的磁光效应, 提出了一种基于光学Tamm态的磁场传感结构。该结构由加载了金属层和电介质层的一维磁流体光子晶体构成。数值研究了该结构的结构参数对传感性能的影响。结果表明, 磁流体层越厚, 探测灵敏度就越高。金属层和电介质层的厚度均存在一个最佳值, 使得传感器具有较高的探测精度。结果还表明, 该传感结构的探测灵敏度优于已报道的采用光子晶体缺陷结构实现的磁场传感器。研究结果为基于光学Tamm态的磁流体磁场传感器的设计制备提供了参考。
光学塔姆态 磁流体 磁场传感 传输矩阵法 optical Tamm state magnetic fluid magnetic field sensors transfer matrix method
中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130033
由于受温度变化的影响, 高分辨力遥感相机焦平面 CCD采样信号的相位会发生变化, 采样位置的温度漂移会严重影响图像的信噪比、动态范围等, 甚至会造成图像无法正常显示。为了解决采样位置随温度漂移的问题, 对高分辨力遥感相机CCD采样位置进行了自适应补偿设计, 首先对CCD采样信号的初始位置进行精密调节, 然后设计了自适应补偿电路, 通过对功耗的控制使各驱动芯片温度基本一致, CCD信号与采样信号在温度变化上具有跟踪性, 在动态上保证CCD信号采样位置的准确性, 从而保证图像信噪比的稳定性。实验表明, 利用该方法, 相关双采样信号的初始位置调节精度小于0.039 ns; 在卫星在轨温度范围内, 相关双采样信号延时最大值为0.46 ns, 保证了相机的高质量成像, 满足航天应用需要。
高分辨力遥感相机 相关双采样 温度 自适应补偿 high-resolution remote sensing cameras Correlated Double Sampling(CDS) temperature adaptive compensation
1 吉林大学电子科学与工程学院, 吉林 长春 130012
2 吉林大学原子与分子物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130012
3 中国科学院超强激光科学研究中心, 上海 201800
近年来,空气激光因在大气传感和环境监测等领域具有重要的潜在应用价值而备受关注。空气激光通常是指强激光诱导大气组分粒子布居数反转,进而产生的远场无腔光放大的激射现象。氮气和氧气作为两种主要的大气组分,均可在强激光激发下产生激射行为。光增益介质可以是氧原子、氮原子、氮分子和氮分子离子。本文以飞秒光丝诱导氮分子和氮分子离子激光为例,讨论了空气激光的现象观测、机理探索和应用前景,并着重介绍了光场偏振效应对氮分子离子激射行为影响的研究进展。
光谱学 空气激光 粒子数反转 大气传感
1 吉林大学电子科学与工程学院, 吉林 长春 130012
2 吉林大学原子与分子研究所, 吉林 长春 130012
聚焦激光脉宽和偏振对飞秒光丝诱导燃烧场中间产物荧光光谱的影响,通过改变激光脉宽、偏振状态,观测了燃烧中间产物如OH、CH、CN、C2分子和C原子的荧光光谱变化。结果发现:随着激光脉宽和偏振椭圆率增大,各组分荧光信号强度减小,这是因为光丝内激光钳制强度及等离子的密度与激光脉宽、偏振密切相关,进而导致多光子激发燃烧中间产物的信号随之变化。
光谱学 飞秒激光成丝 燃烧 荧光 偏振 脉宽
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130033, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049, China
Conventionally, high dynamic-range (HDR) imaging is based on taking two or more pictures of the same scene with different exposure. However, due to a high-speed relative motion between the camera and the scene, it is hard for this technique to be applied to push-broom remote sensing cameras. For the sake of HDR imaging in push-broom remote sensing applications, the present paper proposes an innovative method which can generate HDR images without redundant image sensors or optical components. Specifically, this paper adopts an area array CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) with the digital domain time-delay-integration (DTDI) technology for imaging, instead of adopting more than one row of image sensors, thereby taking more than one picture with different exposure. And then a new HDR image by fusing two original images with a simple algorithm can be achieved. By conducting the experiment, the dynamic range (DR) of the image increases by 26.02dB. The proposed method is proved to be effective and has potential in other imaging applications where there is a relative motion between the cameras and scenes.
Push-broom cameras HDR imaging remote sensing Photonic Sensors
2018, 8(1): 34
采用高温固相法成功制备了Ca3Y2Si3O12∶Tm3+,Yb3+上转换蓝色发光材料。在980 nm 红外激光器激发下, 发光粉呈现强烈的蓝光(475 nm)和近红外光(810 nm)以及较弱的红光(650 nm)发射, 分别归因于Tm3+离子的1G4→3H6、3H4→3H6和1G4→3F4能级跃迁。随着Yb3+离子浓度的增加, 发光粉上转换发射强度和发光亮度均呈现先增强后减弱的变化趋势。在最佳掺杂浓度下(Yb3+摩尔分数为15%), 蓝、红光强度分支比为12∶1, 色坐标为(0.129 2, 0.152 3)。在3.9 W/cm2激发功率密度下, 发光亮度可达6.8 cd/m2。上述结果证实, 所制备发光粉呈现优异的蓝光上转换发射特性并具有潜在的应用价值。发光强度和激发光功率关系表明, 所得上转换发射为三光子和双光子吸收过程。借助Tm-Yb体系能级结构详细讨论了上转换发射的跃迁机制。
上转换发光 硅酸盐 发光粉 980 nm激发 Ca3Y2Si3O12∶Tm3+ Ca3Y2Si3O12∶Tm3+ Yb3+ Yb3+ up-conversion luminescence silicate luminescent powder 980 nm excitation